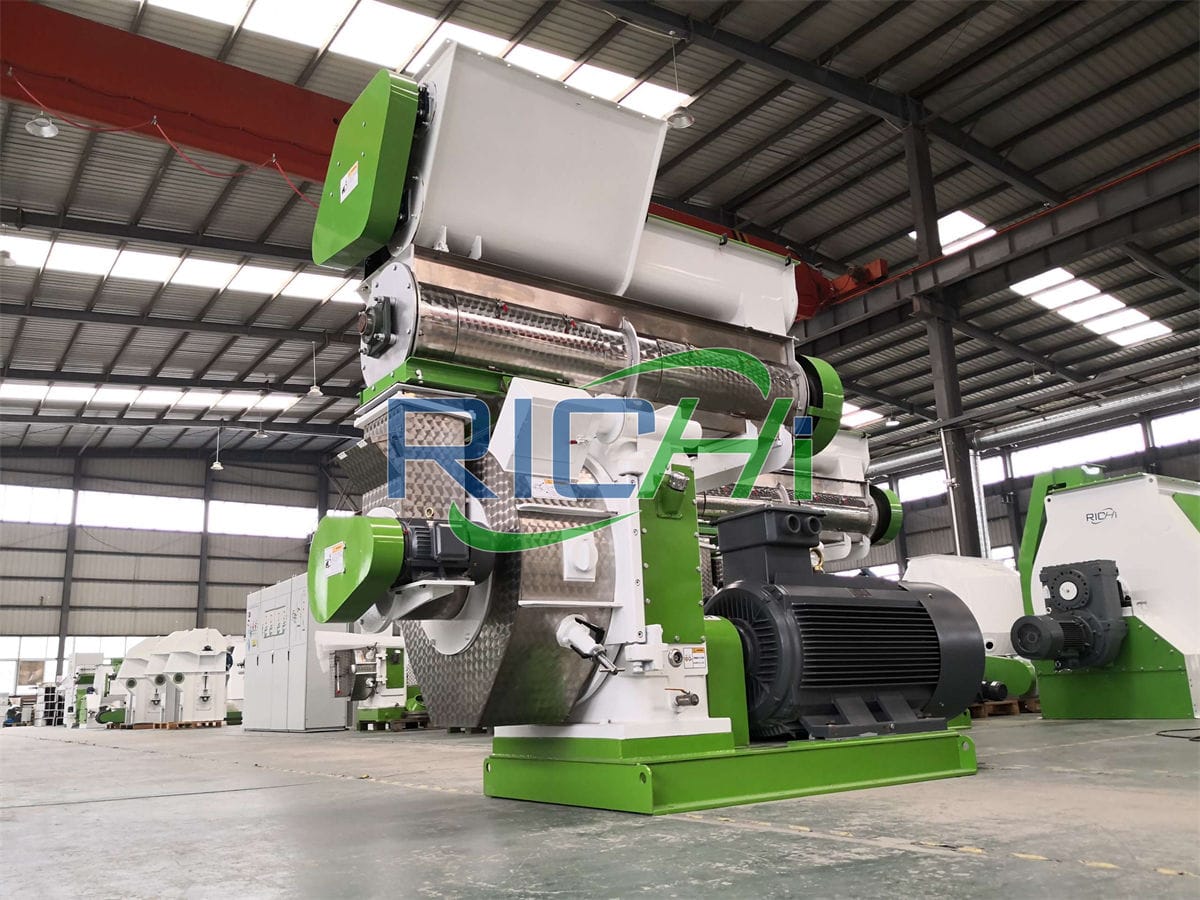
Livestock feed pellet machines are highly versatile tools designed to transform a wide array of feed ingredients into compact, easily digestible pellets. In the context of ruminant feed—intended for animals such as cattle, sheep, goats, and other ruminants with complex digestive systems—these machines play a vital role in the production process. This article examines the capability of livestock feed pellet machines to create ruminant feed pellets, the advantages of pelletized ruminant feed, and the key considerations for their production.
Capability of Livestock Feed Pellet Machines for Ruminant Feed
Livestock feed pellet machines are well-equipped to convert ruminant feed into pellet form. They can process various ingredients commonly included in ruminant diets, such as:
- Fibrous Materials:
- Grass and legume hays
- Crop residues (e.g., corn stalks, wheat straw)
- Silage (after appropriate pre-processing)
- Grains and Concentrates:
- Cereal grains like corn, barley, and wheat
- Protein sources including soybean meal, cottonseed meal, and distillers grains
- Supplements:
- Vitamin and mineral premixes
- Molasses and other liquid additives
The adaptability of livestock feed pellet machines facilitates the formulation of balanced ruminant feed that meets specific nutritional needs.

Benefits of Pelletized Ruminant Feed
Utilizing livestock feed pellet machines to produce pelletized ruminant feed offers several advantages:
- Improved Feed Efficiency:
- Pelletizing can enhance the digestibility of certain feed components, particularly in high-fiber diets, leading to better ruminal fermentation.
- Reduced Feed Waste:
- Pellets are less likely to be sorted or blown away compared to loose feed, resulting in decreased feed loss during handling and feeding.
- Consistent Nutrition:
- Pelletizing ensures uniform distribution of nutrients, which is critical for balanced ruminant diets.
- Enhanced Palatability:
- Many ruminants prefer pellets over mash feeds, potentially increasing feed intake. Pelletizing can also mask the taste of less palatable ingredients.
- Improved Handling and Storage:
- Pellets are more compact, reducing storage space requirements and improving flow in automated feeding systems.
- Incorporation of Difficult Ingredients:
- Pelletizing enables the inclusion of ingredients that may be unpalatable or challenging to mix in loose form.
- Potential for Higher Feed Intake:
- The compact nature of pellets may facilitate higher dry matter intake, benefiting high-producing ruminants.
Considerations for Processing Ruminant Feed Pellets
While livestock feed pellet machines can effectively process ruminant feed, several important factors must be considered:
- Fiber Length:
- Ruminants require a certain amount of long fiber for proper rumen function. Including some long-fiber sources in the diet may be necessary since pelletizing reduces particle size.
- Pellet Hardness:
- Ruminant pellets should be firm enough to maintain integrity during handling but not so hard that they impair palatability or digestion.
- Heat Sensitivity:
- Heat-sensitive nutrients, particularly specific proteins and vitamins, may be impacted by the pelletizing process. Careful temperature control is essential.
- Moisture Content:
- The optimal moisture content for pelletizing (typically 15-17%) must align with the moisture needs of the ruminant diet.
- Pellet Size:
- Pellet size can influence intake and rumination behavior, with different sizes potentially being optimal for various ruminant species or production stages.
- Starch Gelatinization:
- The heat and moisture involved in the pelletizing process can cause starch gelatinization, which may affect rumen fermentation patterns, with varying benefits depending on dietary goals.
- Inclusion of Roughage:
- Although pellet machines can process some fibrous materials, very high inclusion rates of long-fiber ingredients may be difficult to manage.
- Supplemental Feeding:
- Pelletized feeds are often used as supplements to forage-based diets rather than as complete feeds for ruminants. (Related post:animal feed pellet press)
Technological Advancements
Recent developments in livestock feed pellet machine technology have enhanced their capability to produce ruminant feed:
- Variable Die Thickness:
- Allows adjustment of compression ratios to cater to different ruminant feed formulations.
- Improved Conditioning Systems:
- Enhanced control over moisture and temperature during conditioning helps optimize nutrient preservation and pellet quality.
- Dual-Purpose Machines:
- Some manufacturers provide machines that can produce both pellets and extruded feeds, adding flexibility to ruminant feed production.
- Precision Ingredient Dosing:
- Advanced systems enable precise incorporation of micro-ingredients, ensuring consistent nutrient profiles.
Case Studies and Practical Applications
Several successful examples of ruminant feed pellet production using livestock feed pellet machines highlight their effectiveness:
- A dairy farm in California adopted a pelletized concentrate system, reporting increased milk production efficiency and reduced feed waste.
- A sheep operation in Australia developed a drought feed pellet utilizing crop residues and supplements, providing a cost-effective feeding solution during dry periods.
- A beef cattle feedlot in Brazil successfully pelletized a high-roughage finishing diet, noting improved feed conversion rates compared to traditional loose mixed rations.
Nutritional Considerations
When using livestock feed pellet machines to produce ruminant feed, several nutritional factors should be taken into account:
- Effective Fiber:
- Ensuring adequate effective fiber in the overall diet is crucial for maintaining rumen health and function.
- Non-Fiber Carbohydrates:
- Balancing readily fermentable carbohydrates with fiber is essential for optimizing rumen fermentation.
- Protein Degradability:
- The effects of heat treatment during pelletizing on protein degradability in the rumen must be considered.
- Mineral Availability:
- It is important to ensure that mineral supplements remain available and do not negatively interact during the pelletizing process.
Conclusion
Livestock feed pellet machines are indeed capable of producing high-quality ruminant feed pellets. This capability offers numerous benefits, including improved feed efficiency, consistency, and management for ruminant livestock operations. The ability to create balanced, nutrient-dense pellets contributes to enhanced animal performance and operational efficiency.
However, successful ruminant feed pellet production necessitates careful consideration of the unique digestive needs of ruminants, particularly concerning fiber requirements and rumen function. Proper formulation, machine operation, and integration with overall feeding programs are essential to fully realize the advantages of pelletized ruminant feeds.
As technology continues to evolve and our understanding of ruminant nutrition deepens, we can anticipate further improvements in the use of livestock feed pellet machines for ruminant feed production. This ongoing development promises to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of ruminant livestock production systems worldwide.