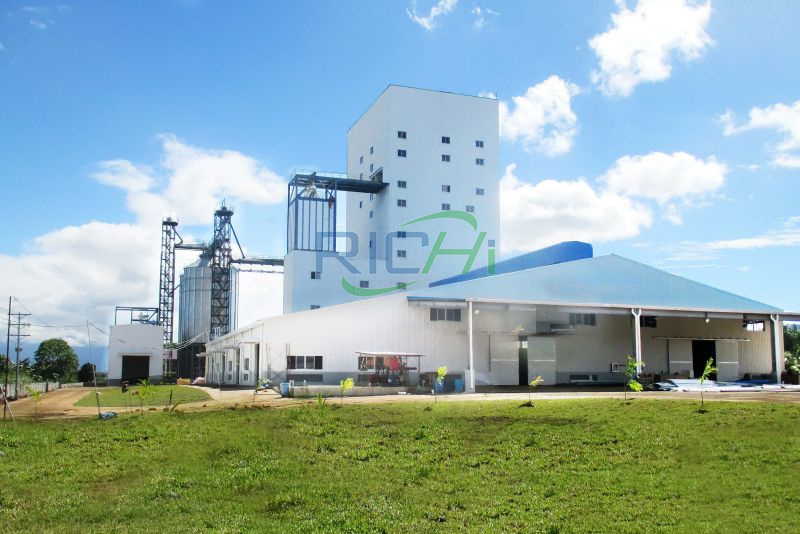
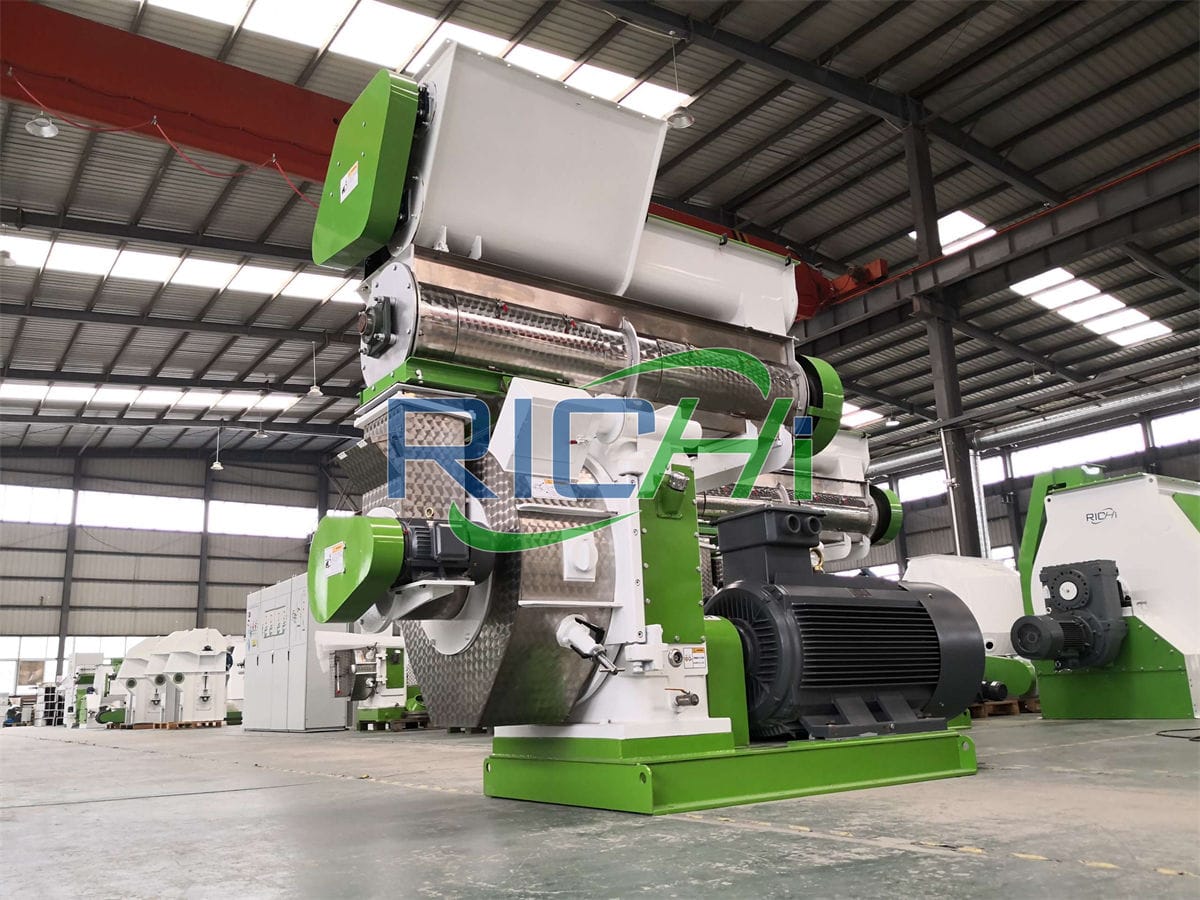
The production process of a premix feed mill is a meticulous and detailed operation designed to ensure the delivery of high-quality, nutrient-rich products that enhance animal nutrition. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. Raw Material Selection and Procurement
- Key Ingredients: Vitamins (A, D, E, K, B-complex, C), minerals (calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, iron, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium, iodine), amino acids (lysine, methionine, threonine, tryptophan), enzymes (phytases, carbohydrases, proteases), probiotics, prebiotics, antioxidants, acidifiers, and mycotoxin binders.
- Procurement: Ingredients are sourced from reputable suppliers to meet strict quality standards, ensuring they are free from contaminants.
2. Quality Control and Testing
- Tests Performed: Nutrient analysis, microbiological testing, physical inspection, and chemical analysis.
- Objective: Ensures only high-quality ingredients proceed to the next stage by verifying nutrient content, detecting pathogens, and identifying contaminants.
3. Ingredient Storage
- Storage Conditions: Temperature and humidity control, protection from light.
- Purpose: Maintains the integrity and stability of raw materials, particularly those sensitive to heat, moisture, or light.
4. Weighing and Dosing
- Process: Ingredients are weighed and dosed accurately using precision scales and automated dosing systems.
- Importance: Ensures correct formulation and consistency, with all weights and batch numbers recorded for traceability.
5. Mixing
- Stages:
- Micro Mixing: Small quantities of concentrated ingredients are mixed using specialized mixers for a uniform blend.
- Macro Mixing: Larger quantities of carrier materials are mixed with the micro mix to achieve a homogeneous final product.
- Objective: Achieves a low coefficient of variation (CV), indicating even distribution of ingredients.

6. Quality Control and Sampling
- Sampling: Representative samples are taken from each batch.
- Testing: Nutrient analysis, physical, and chemical tests are conducted to ensure product consistency and compliance with specifications.
7. Packaging
- Materials: Packaging materials are chosen to protect the premix from moisture, light, and contamination.
- Process: Automated systems are used for bagging, sealing, and labeling, ensuring accuracy and efficiency. (Related post:automatic cattle feed plant)
8. Storage and Distribution
- Storage Conditions: Controlled temperature and humidity, protection from pests.
- Distribution: Timely delivery to feed manufacturers, farmers, or end-users is essential for maintaining product quality.
9. Documentation and Traceability
- Records Maintained: Source and batch numbers of raw materials, process documentation, quality control test results.
- Purpose: Ensures traceability from raw materials to the final product, critical for quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
10. Regulatory Compliance
- Standards Followed: Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), and local regulations for feed additives and premixes.
- Inspections: Regular audits by regulatory authorities ensure compliance and uphold the mill’s credibility.
Conclusion
Every stage in the production process of a premix feed mill is vital for ensuring the final product meets the high standards required in animal nutrition. By following these key steps, premix feed mills contribute to the health, growth, and productivity of livestock, fulfilling the demands of the agricultural industry and supporting animal well-being globally.